Ginseng and “Shanghuo” (fireness): a comprehensive review from the viewpoints of TCM theory and modern science
Abstract
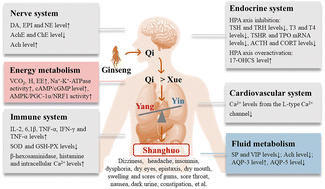
Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer is a type of plant resource that has been used as both a traditional medicine and food for thousands of years. Although ginseng has been used widely, people in China are often concerned that the long-term use or overdose of ginseng might cause a series of mild adverse effects such as insomnia, dizziness, dysphoria and dryness of mouth and eyes, which are commonly known as “Shanghuo” ( ) according to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory. This review summarizes relevant studies on ginseng and “Shanghuo” and tries to elucidate the relationship between them from both traditional and modern science perspectives. Ginseng-induced “Shanghuo” is mainly driven by the hot property of the drug according to TCM theory, and it is believed to be related to energy metabolism and the endocrine, immune and cardiovascular systems. Ginsenosides such as Rf, Rh1 and Rg2 may play important roles in inducing “Shanghuo”, as the physiological effects of these compounds are similar to the biochemical changes observed during “Shanghuo”. It is still under debate whether the improper use of ginseng causes “Shanghuo”, since “Shanghuo” is dependent on the dosage of the drug, the TCM constitution type and other factors. This study provides insights into ginseng and “Shanghuo” from the perspective of TCM theory and modern medicine, along with its potential mechanisms, helping to provide safe and rational use of ginseng.
) according to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory. This review summarizes relevant studies on ginseng and “Shanghuo” and tries to elucidate the relationship between them from both traditional and modern science perspectives. Ginseng-induced “Shanghuo” is mainly driven by the hot property of the drug according to TCM theory, and it is believed to be related to energy metabolism and the endocrine, immune and cardiovascular systems. Ginsenosides such as Rf, Rh1 and Rg2 may play important roles in inducing “Shanghuo”, as the physiological effects of these compounds are similar to the biochemical changes observed during “Shanghuo”. It is still under debate whether the improper use of ginseng causes “Shanghuo”, since “Shanghuo” is dependent on the dosage of the drug, the TCM constitution type and other factors. This study provides insights into ginseng and “Shanghuo” from the perspective of TCM theory and modern medicine, along with its potential mechanisms, helping to provide safe and rational use of ginseng.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Review Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...