l-Carnitine and synbiotic co-supplementation: beneficial effects on metabolic-endotoxemia, meta-inflammation, and oxidative-stress biomarkers in obese patients: a double blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial
Abstract
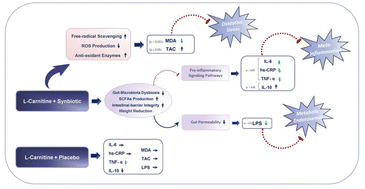
Obesity, a chronic pandemic disease, is characterized by low-grade chronic inflammation, accompanied by over-expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby contributing to metabolic disorders pathogenesis. Oxidative-stress, an adverse cellular response to adipocyte hypertrophy, promotes inflammation. Furthermore, gut-microbiota dysbiosis may induce oxidative-stress, low-grade inflammation, and metabolic-endotoxemia as major drivers of obesity. Functional-foods/nutraceuticals have attracted extensive attention due to their plausible anti-inflammatory/anti-oxidative properties; evidence supports the superiority of the nutraceutical combined-supplementation approach versus conventional mono-therapies. Current data suggest the anti-oxidative/anti-inflammatory properties of either L-carnitine or pre/pro/synbiotics. This trial compared the effects of co-supplementing L-carnitine and multi-species/multi-strain synbiotic versusL-carnitine mono-therapy on inflammatory/anti-inflammatory, oxidative-stress, and metabolic-endotoxemia biomarkers in 46 female obese patients, receiving either co-supplementation (L-carnitine-tartrate (2 × 500 mg d−1) + multi-species/multi-strain synbiotic (1 capsule per day)) or mono-therapy (L-carnitine-tartrate (2 × 500 mg d−1) + maltodextrin (1 capsule per day)) for eight weeks. L-Carnitine + synbiotic co-supplementation significantly decreased interleukin-6 (IL-6, −33.98%), high-sensitivity-C-reactive-protein (hs-CRP, −10%), tumor-necrosis-factor-alpha (TNF-α, −18.73%), malondialdehyde (MDA, −21.73%), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS, −10.14%), whereas the increase in interleukin-10 (IL-10, 7.69%) and total-antioxidant-capacity (TAC, 4.13%) levels was not significant. No significant changes were observed for the above-mentioned parameters in the L-carnitine + placebo group, except for a significant reduction in IL-10 (−17.59%) and TNF-α (−14.78%); however, between-group differences did not reach the significant threshold. Co-supplementing L-carnitine + multi-strain synbiotic led to significant amelioration of inflammatory, oxidative, and metabolic-endotoxemia responses in female obese patients; nevertheless, no improving effects were observed in patients receiving single-supplementation, suggesting that L-carnitine + synbiotic co-supplementation might represent an adjuvant approach to improve oxidative-stress/pro-inflammatory indicators in women with obesity, possibly through beneficial effects of the synbiotic alone. Further longer duration studies with higher doses of L-carnitine in a three-group setting are warranted to elucidate the possibility of synergistic or complementary mechanisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...