Screening of anti-liver fibrosis peptides from turtle shell protein using two-enzyme hydrolysis by molecular docking†
Abstract
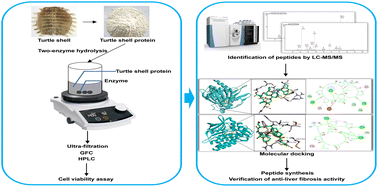
Turtle shell as a food residue of Pelodiscus sinensis (a type of edible aquatic animal) is widely used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for hepatic fibrosis therapy. Previous studies have demonstrated that the peptides (<6 kDa) derived from turtle shells are considered effective components. The protein of turtle shells has important potential as a source of bioactive peptides which may play a role as ingredients in functional foods. In the present study, the protein of turtle shell was hydrolyzed using a two-enzyme combination. It was found that the hydrolysates obtained by a combination of pepsin and trypsin showed the highest anti-liver fibrosis activity relative to other combinations in a cell viability assay. The hydrolysates were separated and purified by ultra-filtration (<6 kDa), gel filtration chromatography (GFC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Subsequently, the sequences of purified peptides were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Molecular docking was used to analyze the interaction of these peptides with the transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) receptor. Two (GPPGVPGPGPL, TSLPVPAPV) of these novel peptides displayed lower binding energies to the TGF-β1 receptor (−8.18 kcal mol−1, −8 kcal mol−1). Finally, the above two peptides were synthesized chemically and their in vitro anti-liver fibrosis activity was verified by MTT assay. Among them, GPPGVPGPGPL showed a better in vitro anti-liver fibrosis activity (IC50: 80.13 μM). We established a method to obtain anti-liver fibrosis peptides from turtle shells by using bioactivity-guided isolation with molecular docking. Turtle shell protein is an excellent source of anti-liver fibrosis peptides which can offer therapeutic and commercial benefits as an ingredient in functional foods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...