Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activities of Castanopsis honey†
Abstract
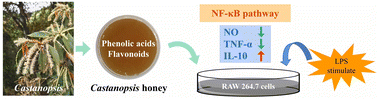
Castanopsis is diffusely spread in tropical and subtropical regions and is an important nectar source plant in China. The Castanopsis honey (CH) is characterized by its bitter taste. However, its composition and functions remain unclear. In this study, the physicochemical parameters, chemical composition, and antioxidant capacity of CH were comprehensively investigated, with the anti-inflammatory effects of the Castanopsis honey extract (CHE) evaluated based on the RAW 264.7 cell inflammatory model. The results revealed a high level of quality in CH based on the quality standards. Among a total of 84 compounds identified in CH, 5 high response compounds and 29 phenols were further quantified by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. The high content of phenylethylamine (117.58 ± 64.81 mg kg−1) was identified as a potential marker of CH. Furthermore, the CH showed evident antioxidant activities, and the anti-inflammatory activities of CHE were observed to inhibit the release of nitric oxide (NO) and reduce the content of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and improve the content of interleukin-10 (IL-10) by regulating the NF-κB pathway. Our study indicates that CH has sound physicochemical properties and biological activities with a high level of quality, providing strong experimental evidence to support the further economic and agricultural development and application of CH.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...