Okanin from Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. alleviates cognitive impairment in bilateral common carotid artery occlusion mice by regulating the miR-7/NLRP3 axis in microglia†
Abstract
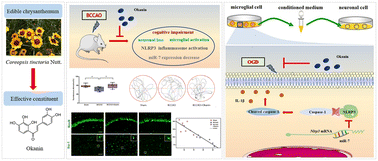
Cognitive impairment is the main clinical feature following stroke, and microglia-mediated inflammatory response is a major contributor to it. Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt., an edible chrysanthemum, is commonly used as a functional ingredient in healthcare beverages and food. Okanin, the main active ingredient of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. flower, inhibits microglial activation. However, the role of okanin in cognitive impairment following ischemic stroke is still unknown. In this study, we investigated the effect of okanin on ischemic stroke and its underlying mechanism both in vivo and in vitro. Okanin was found to attenuate cognitive impairment in bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) mice, inhibit neuronal loss and microglial activation, decrease NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, and increase miR-7 expression. Okanin suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated microglia by increasing miR-7 expression and inhibited microglia-induced neuronal injury. This study provides new insights into the role of okanin in ischemic stroke and shows that the miR-7/NLRP3 axis plays an important role in mediating the beneficial effects of okanin on cerebral ischemia. These findings suggest that okanin has great potential as a functional food for stroke recovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...