Antioxidant N-acetylcysteine removing ROS: an antifouling strategy inspired by mussels†
Abstract
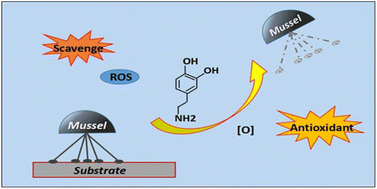
Marine biofouling is a thorny issue that causes serious economic losses and adverse ecological impacts on marine ecosystems. Effective and promising antifouling strategies such as surface hydration, flow shear force, and lubricant injection have been developed to address this challenge. However, for the complex marine environment, they still appear inadequate. Mussels are a common fouling organism with strong surface adhesion ability. However, when hypoxia and the oxidative cross-linking reaction of 3,4-dihydroxy phenyl-L-alanine (DOPA) in the structure of adhesion proteins are disrupted, their adhesion ability will be greatly reduced. Inspired by this, we developed an effective antifouling strategy based on reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging using N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and evaluated its performance. As a ROS scavenger interfered with the oxidative cross-linking reaction of DOPA in an aqueous solution, the adhesion of DOPA was also affected on the surface of NAC functionalized polyvinyl chloride (PVC) (PVC-NAC). In addition, the colonization level of mussels and the adhesion rate of marine bacteria and benthic diatoms on PVC-NAC were low. The antifouling strategy proposed in this paper was eco-friendly and broad-spectrum, and may provide a new idea for solving marine biofouling and reducing the environmental and economic impacts of fouling organisms.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts Recent HOT Articles and Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...