Combined, time-resolved, in situ neutron reflectometry and X-ray diffraction analysis of dynamic SEI formation during electrochemical N2 reduction†
Abstract
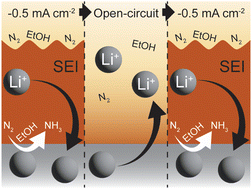
One means of improving performance for electrochemical ammonia production through the Li-mediated N2 reduction reaction (Li-NRR) is by cycling the current driving the reaction between open-circuit conditions and periods of applied current density. Herein, we have investigated the dynamics of the electrode–electrolyte interface under Li-NRR conditions during current cycling using in situ time-resolved neutron reflectometry and grazing-incidence synchrotron X-ray diffraction. During cycling, measured neutron reflectivity curves indicated bilayer formation in which Li-containing species such as LiOH, Li2O, and small quantities of Li3N and metallic Li primarily appeared in a thin layer at the cathode surface, above which formed a much larger, porous, ‘solid–electrolyte interface’ (SEI) layer. Upon return to open-circuit conditions, Li-containing species quickly moved out of the thin layer, leaving a compact, stable layer of decomposition products underneath the SEI layer. This SEI layer concomitantly filled with electrolyte or dissolved, becoming indistinguishable from the electrolyte via contrast in scattering-length density (SLD). During the second current cycle, Li-containing species again preferentially deposited directly atop the cathode, with the thick SEI-like layer again appearing within a minute. This SEI layer exhibited a lower SLD more quickly than in the first cycle, which might suggest that Li-containing species become distributed within the porous SEI layer. Thus, these time-resolved observations of SEI and plated layers during current cycling suggest that benefits associated with return to open-circuit conditions between periods of applied current density may be related to the concomitant loss of Li-containing species from a thin layer at the cathode surface into a porous SEI layer that becomes filled with electrolyte or dissolves.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...