Enhancing the performance of Cu catalysts for the reverse water–gas shift reaction using N-doped CNT–ZnO composite as support†
Abstract
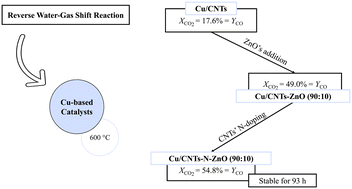
The reverse water–gas shift reaction (RWGS) allows the conversion of CO2 to CO which, mixed with H2, forms syngas, the feedstock of most chemicals and synthetic fuels production. Consequently, it is crucial to develop efficient catalysts for this reaction. To further the development of RWGS catalysts, Cu-based catalysts supported on pristine CNTs and on composites of pristine and functionalized CNTs : ZnO were prepared. ZnO's presence in the catalyst's structure proved to be beneficial, as the CO2 conversion and CO yield reached 49.0% whereas the catalysts supported on pristine CNTs only achieved a CO2 conversion and CO yield of 17.6%, at a temperature of 600 °C. The N-doping of CNTs further improved the CO2 conversion and CO yield to 54.8%, remaining stable at least for 93 h.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...