Thermal chemical vapor deposition of layered carbon nitride films under a hydrogen gas atmosphere†
Abstract
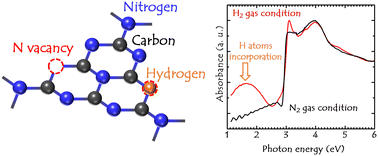
We prepared layered carbon nitride (g-C3N4) films via thermal chemical vapor deposition under an atmosphere of nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2). Crystalline films ordered along the layered stacking direction were deposited using melamine powder as a precursor. A deposition rate of >3 μm was achieved at a synthesis temperature of 575 °C. The bonding states analyzed via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated the inclusion of H atoms in the g-C3N4 films. The number of H-related bonds, such as C–NHx and C–NH2, was greater for the deposition under a H2 gas atmosphere than that under a N2 gas flow and increased with increasing substrate temperature. In addition to the typical feature of g-C3N4 at an absorption edge of 2.80 eV, the energy state originating from the H-incorporation at ∼ 1.70 eV was observed for the deposition under H2 gas conditions. Furthermore, the energy of the absorption edge was reduced to 2.05 eV when the substrate temperature was increased to 600 °C. The photoluminescence (PL) characteristics at the peak position were not significantly different, regardless of the temperature and flow gas used. Notably, the PL spectral width for the deposition under a H2 gas atmosphere was narrower than that for the deposition under a N2 gas atmosphere.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...