Spinel Li4Ti5O12 hollow nanospheres prepared with colloid carbon spheres as templates for high power Li-ion battery anodes
Abstract
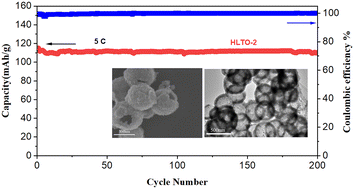
Spinel Li4Ti5O12 hollow nanospheres self-assembled with lamellar nanocrystallites have been successfully prepared by employing colloid carbon spheres as templates via a solvothermal reaction route and a subsequent calcination process. During the solvothermal treatment, the amorphous Li4Ti5O12 deposits on the colloid carbon spheres, leading to amorphous C@a-Li4Ti5O12 core–shell nanospheres. Two calcination strategies, one is to calcine the C@a-Li4Ti5O12 core–shell nanospheres in air directly and the other is to first calcine the nanospheres in inert gas of nitrogen and then in air, are investigated for controlling the microstructures of spinel Li4Ti5O12 hollow nanospheres. Based on the experimental results, the formation mechanism of the spinel Li4Ti5O12 hollow nanospheres has been discussed. The spinel Li4Ti5O12 hollow nanospheres obtained by the secondary calcination method exhibit nice capacity retention and high-rate capacity due to the smaller lamellar nanocrystallites and enhanced contact with the electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...