Fluorescent liposomal nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in ischemic stroke therapy
Abstract
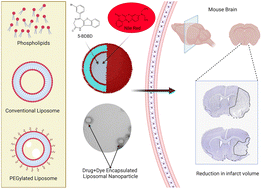
Ischemic stroke causes acute CNS injury and long-term disability, with limited treatment options such as surgical clot removal or clot-busting drugs. Neuroprotective therapies are needed to protect vulnerable brain regions. The purinergic receptor P2X4 is activated during stroke and exacerbates post-stroke damage. The chemical compound 5-(3-Bromophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-Benzofuro[3,2-e]-1,4-diazepin-2-one (5BDBD) inhibits P2X4 and has shown neuroprotective effects in rodents. However, it is difficult to formulate for systemic delivery to the CNS. The current manuscript reports for the first time, the synthesis and characterization of 5BDBD PEGylated liposomal formulations and evaluates their feasibility to treat stroke in a preclinical mice model. A PEGylated liposomal formulation of 5BDBD was synthesized and characterized, with encapsulation efficacy of >80%, and release over 48 hours. In vitro and in vivo experiments with Nile red encapsulation showed cytocompatibility and CNS infiltration of nanocarriers. Administered 4 or 28 hours after stroke onset, the nanoformulation provided significant neuroprotection, reducing infarct volume by ∼50% compared to controls. It outperformed orally-administered 5BDBD with a lower dose and shorter treatment duration, suggesting precise delivery by nanoformulation improves outcomes. The fluorescent nanoformulations may serve as a platform for delivering and tracking therapeutic agents for stroke treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...