Combinatorial extracellular matrix cues with mechanical strain induce differential effects on myogenesis in vitro†
Abstract
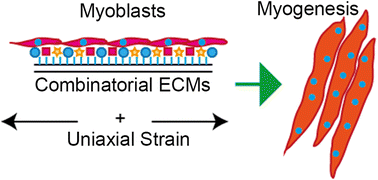
Skeletal muscle regeneration remains a clinical unmet need for volumetric muscle loss and atrophy where muscle function cannot be restored to prior capacity. Current experimental approaches do not account for the complex microenvironmental factors that modulate myogenesis. In this study we developed a biomimetic tissue chip platform to systematically study the combined effects of the extracellular matrix (ECM) microenvironment and mechanical strain on myogenesis of murine myoblasts. Using stretchable tissue chips composed of collagen I (C), fibronectin (F) and laminin (L), as well as their combinations thereof, we tested the addition of mechanical strain regimens on myogenesis at the transcriptomic and translational levels. Our results show that ECMs have a significant effect on myotube formation in C2C12 murine myoblasts. Under static conditions, laminin substrates induced the longest myotubes, whereas fibronectin produced the widest myotubes. Combinatorial ECMs showed non-intuitive effects on myotube formation. Genome-wide analysis revealed the upregulation in actin cytoskeletal related genes that are suggestive of myogenesis. When mechanical strain was introduced to C + F + L combinatorial ECM substrates in the form of constant or intermittent uniaxial strain at low (5%) and high (15%) levels, we observed synergistic enhancements in myotube width, along with transcriptomic upregulation in myosin heavy chain genes. Together, these studies highlight the complex role of microenvironmental factors such as ECM interactions and strain on myotube formation and the underlying signaling pathways.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biomaterials Science 10th Anniversary Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...