Crystal plane-integrated strontium oxide/hexagonal boron nitride nanohybrids for rapid electrochemical sensing of anticancer drugs in human blood serum samples†
Abstract
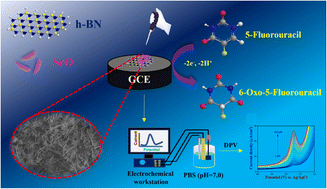
In this work, the crystal plane of strontium oxide (SrO) nanorods was integrated into hexagonal-boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheets to form 1D–2D (SrO/h-BN) composite were utilized for the electrochemical detection of the chemotherapeutic drug 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu). 5-Fu is a clinically proven and the third most frequently applied chemotherapeutic drug for treating solid tumours, such as colorectal, stomach, cutaneous and breast malignancies. Its overdoses lead to toxic metabolite accumulation that has serious adverse consequences on humans, including neurotoxicity, death and the induction of morbidity. Therefore, to improve the chemotherapy and predict the potential adverse effects of 5-Fu residues in the human body, susceptible and quick analytical methods for detecting 5-Fu in human body fluids (blood serum/plasma and urine) are needed. The effective interaction of the synthesized SrO/h-BN composite shows increased efficiency for the electrochemical detection of 5-Fu with good selectivity. Notably, a simple sonochemical method achieved a synergistic interaction between the (100) plane of SrO and the (002) plane of h-BN. Various analytical and spectroscopic techniques were used to characterize the SrO/h-BN nanocomposite, which provided useful insights into the composition and properties of the composite material. The crystalline, structural and chemical characteristics of the as-synthesized material were characterized by XRD, Raman spectroscopy, HR-TEM, XPS and HR-SEM. Furthermore, the proposed electrode's electrochemical sensing capability was analysed using CV, EIS, DPV and i–t curve methods. Numerous active sites created on a modified electrode enhanced the mass transport and electron transfer rate, thereby increasing the electrochemical activity towards the 5-Fu detection. Consequently, under optimized conditions, the SrO/h-BN/GCE exhibited remarkable selectivity, durability, low detection limit (0.003 μM) and wide linear range (0.02–56 μM) for 5-Fu. Finally, the successful application of this sensor for 5-Fu detection in biological samples was successfully tested with high recovery percentages.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...