Discrimination of whole grape juice using fluorescence spectroscopy data with linear discriminant analysis coupled to genetic and ant colony optimisation algorithms
Abstract
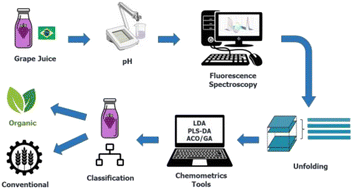
In this study, a new approach was developed for classifying grape juices produced in Brazil using unfolded excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy and chemometrics, with respect to the agricultural production system, namely the conventional or organic agricultural one. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) coupled to ant colony optimisation (ACO) and the genetic algorithm (GA) were used to select a more effective subset of variables to discriminate grape juice samples. The best results demonstrated highly efficient classification of grape juice samples according to a conventional or organic production process with an accuracy rate of up to 97% for the models and 94% in the prediction of these classes for samples external to the model. The models showed high selectivity and sensitivity with a rate of up to 100% for the training and test datasets, in addition to determining the most significant variables that explain the separation of classes. The proposed method proves to be viable, as it is fast and requires minimal sample preparation, allowing quality control in the food industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...