Biomass-derived magnetic nanocomposites modified by choline chloride/citric acid based natural deep eutectic solvents for the magnetic solid phase extraction of trypsin
Abstract
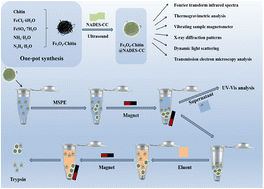
A novel biomass-derived magnetic nanocomposite of Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC composed of a natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES), biological polysaccharide (Chitin) and magnetic Fe3O4 was synthesized. After being systematically characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, thermogravimetry, vibrating sample magnetometry, X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering, Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC was used as an extractant to separate trypsin (Tryp) on the basis of magnetic solid phase extraction. Simultaneously, the extraction conditions of Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC for Tryp were investigated in turn by single-factor experiments, including screening the types of extractants, the initial concentration of Tryp, the pH value of the solution, the influence of ionic strength, extraction time and temperature, etc. Under the optimal conditions, the extraction capacity of Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC for Tryp could reach up to 1082.67 mg g−1. Adsorption isotherm tests certified that the Langmuir adsorption equilibrium fitted well with the extraction model in this study, which showed that the extraction of Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC for Tryp was monolayer adsorption. In addition, in the sections on the regeneration–reuse, selectivity and methodological studies, all the results exhibited the superiority of the Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC and Tryp separation strategy which has been established in this work. Finally, Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC was ultimately applied to the separation of Tryp from a real bovine pancreas crude extract by the analysis of SDS-PAGE. All the above results highlight that the proposed Fe3O4-Chitin@NADES-CC biomass-derived magnetic nanocomposite can be applied in the field of protein purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...