An ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for phospholipase C via signal amplification based on breathing ATRP and its application†
Abstract
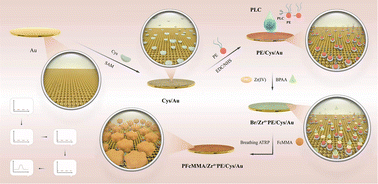
Phospholipase C (PLC) has important biological functions in specific cancer types, immune disorders and neurodegeneration. Here, an ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for PLC was developed via signal amplification based on breathing atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). First, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) was immobilized on the surface of a gold electrode by L-cysteine and cross-linker. Then, PE was specially hydrolyzed by PLC to obtain the phosphate groups and tethered with the ATRP initiator α-bromophenacetic acid (BPAA) by the coordination action of Zr4+. After the breathing ATRP, a large number of electroactive monomers (ferrocenylmethyl methacrylate, FcMMA) were successfully grafted from BPAA. The experimental results indicated that the detection signal of the obtained electrode (sensor) was proportional to the concentration of PLC. The sensor showed a low detection limit of 0.270 U L−1 and a wide linear range of 1–40 U L−1 (R2 = 0.997). Most importantly, the sensor was successfully applied to detect PLC in breast cancer cells (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231) and nontumor cells (MCF-10A). The value obtained by our electrochemical sensor had no obvious difference from that determined by the commercial ELISA kit. These results showed that the fabricated PLC sensor had acceptable potential in clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...