Surface modified materials for active capture of enzymes†
Abstract
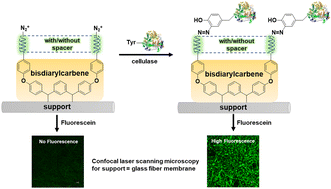
The insertion of bis(diarylcarbene)s onto a glass fiber (GF) membrane surface provided an active coating for the direct capture of protein – exemplified by the enzyme, cellulase – through a mild diazonium coupling process which does not require additional coupling agents. Successful cellulase attachment on the surface was demonstrated by the disappearance of diazonium and formation of azo functions in the N 1s high resolution spectra, the appearance of carboxyl group in C 1s spectra, both observed by XPS; the –C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O vibrational bond observed by ATR-IR; as well as the observation of fluorescence. Further, five support materials (polystyrene XAD4 bead, polyacrylate MAC3 bead, glass wool, glass fiber membrane, polytetrafluoroethylene membrane) with different morphology and surface chemistry, were examined in detail as supports for cellulase immobilization using this common surface modification protocol. Of interest is that such covalently bound cellulase on modified GF membrane gave both the highest enzyme loading (∼23 mg cellulase per g support), and retained more than 90% of activity after 6 cycles of re-use, compared with substantial loss of enzyme activity for physiosorbed cellulase after 3 cycles. Optimization of the degree of surface grafting and the effectiveness of a spacer between surface and enzyme for enzyme loading and activity were conducted. This work shows that carbene surface modification is a viable strategy for introducing enzymes onto a surface under very mild conditions and retaining a meaningful level of activity, and particularly, using GF membrane as a novel support provides a potential platform for enzyme and protein immobilization.
O vibrational bond observed by ATR-IR; as well as the observation of fluorescence. Further, five support materials (polystyrene XAD4 bead, polyacrylate MAC3 bead, glass wool, glass fiber membrane, polytetrafluoroethylene membrane) with different morphology and surface chemistry, were examined in detail as supports for cellulase immobilization using this common surface modification protocol. Of interest is that such covalently bound cellulase on modified GF membrane gave both the highest enzyme loading (∼23 mg cellulase per g support), and retained more than 90% of activity after 6 cycles of re-use, compared with substantial loss of enzyme activity for physiosorbed cellulase after 3 cycles. Optimization of the degree of surface grafting and the effectiveness of a spacer between surface and enzyme for enzyme loading and activity were conducted. This work shows that carbene surface modification is a viable strategy for introducing enzymes onto a surface under very mild conditions and retaining a meaningful level of activity, and particularly, using GF membrane as a novel support provides a potential platform for enzyme and protein immobilization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: #MyFirstJMCB


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...