Post-imprinting modification: electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy studies of a semi-covalently surface imprinted polymer†
Abstract
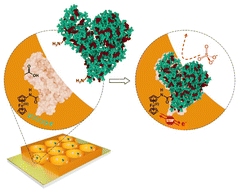
Herein we described a post-imprinting modification of the imprinted molecular cavities for electrochemical sensing of a target protein. Imprinted molecular cavities were generated by following the semi-covalent surface imprinting approach. These mesoporous cavities were modified with a ferrocene ‘electrochemical’ tracer for electrochemical transduction of the target protein recognition. Electrochemical sensors prepared after post-imprinting modification showed a linear response in the concentration range of 0.5 to 50 μM. Chemosensors fabricated based on capacitive impedimetric transduction demonstrated that imprinted molecular cavities without post-imprinting modification showed better selectivity. Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) was used for the surface characterization of imprinted molecular cavities modified with ferrocene electrochemical tracers. SECM analysis performed in the feedback mode monitor changes in the surface state of the ferrocene-modified polymer film. The kinetics of the mediator regeneration was almost 1.8 times higher on the non-imprinted surface versus the post-imprinting modified molecular imprinted polymer.
- This article is part of the themed collections: 2023 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Most Popular Articles and Editor’s Choice: Kaushik Chatterjee


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...