Citrated cellulose nanocrystals from post-consumer cotton textiles†
Abstract
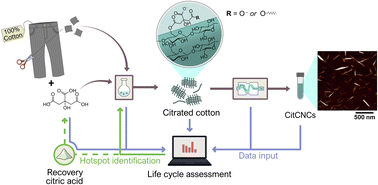
We propose a new method for the extraction of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) from post-consumer cotton textiles through surface functionalization followed by mechanical treatment. Cotton-based textiles were esterified using an 85 wt% solution of citric acid at 100 °C, then further fibrillated in a microfluidizer. The final product, citrated cellulose nanocrystals (CitCNCs), was a dispersion of needle-like nanoparticles with high crystallinity. Up to 78 wt% of the cotton fabric was converted to CitCNCs that exhibited higher yields and a higher surface group content than CNCs extracted through H2SO4 hydrolysis, although CitCNCs showed a broader size distribution and decreased thermal stability. Experimental data supported by DFT calculations showed that the carboxyl groups on the CitCNC surface are bonded to cellulose by mono or diester linkages. An early-stage life cycle assessment (LCA) was performed to evaluate the environmental impact of using discarded textiles as a source of cellulose and analyze the environmental performance of the production of CitCNCs. Our work showed a significant reduction in the environmental burden of CNC extraction using post-consumer cotton instead of wood pulp, making clothing a good feedstock. The environmental impact of CitCNC production was mainly dominated by citric acid. As a proof of concept, around 58 wt% of the citric acid was recovered through evaporation and subsequent crystallization, which could reduce climate impact by 40%. With this work, we introduce a catalyst-free route to valorize textiles with the extraction of CitCNCs and how conducting LCA in laboratory-scale processes might guide future development and optimization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...