Modulation of wetting of stimulus responsive polymer brushes by lipid vesicles: experiments and simulations†
Abstract
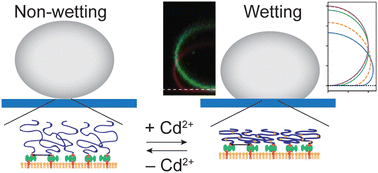
The interactions between vesicle and substrate have been studied by simulation and experiment. We grafted polyacrylic acid brushes containing cysteine side chains at a defined area density on planar lipid membranes. Specular X-ray reflectivity data indicated that the addition of Cd2+ ions induces the compaction of the polymer brush layer and modulates the adhesion of lipid vesicles. Using microinterferometry imaging, we determined the onset level, [CdCl2] = 0.25 mM, at which the wetting of the vesicle emerges. The characteristics of the interactions between vesicle and brush were quantitatively evaluated by the shape of the vesicle near the substrate and height fluctuations of the membrane in contact with brushes. To analyze these experiments, we have systematically studied the shape and adhesion of axially symmetric vesicles for finite-range membrane–substrate interaction, i.e., a relevant experimental characteristic, through simulations. The wetting of vesicles sensitively depends on the interaction range and the approximate estimates of the capillary length change significantly, depending on the adhesion strength. We found, however, that the local transversality condition that relates the maximal curvature at the edge of the adhesion zone to the adhesion strength remains rather accurate even for a finite interaction range as long as the vesicle is large compared to the interaction range.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...