Development of water-soluble phenazine-2,3-diol-based photosensitizers for singlet oxygen generation†
Abstract
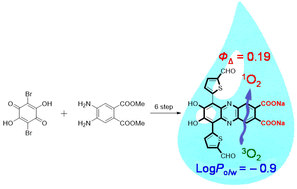
Phenazine-2,3-diol-based dyes, KY-1Na and KY-2Na bearing one and two carboxylic acid sodium salts, respectively, have been newly developed as water-soluble photosensitizers (PSs) possessing the ability to generate singlet oxygen (1O2). In order to evaluate the solubility of KY-1Na and KY-2Na in water, the hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity of the two PSs was investigated by experimental measurement of the logarithms (log Po/w) of the 1-octanol/water partition coefficient (Po/w) for the PS. The log Po/w values of both KY-1Na and KY-2Na were determined to be −0.9, indicating that both the PSs are more hydrophilic than Rose Bengal (−0.6) and have hydrophilicity equivalent to methylene blue (−0.9). Both the PSs in water show a broad photoabsorption band in the range of 500 to 600 nm. Thus, we estimated the 1O2 quantum yields (ΦΔ) of KY-1Na and KY-2Na in water by using 9,10-anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABDA) as a water-soluble 1O2 scavenger. It was found that in water the ΦΔ value (0.19) of KY-2Na is higher than that of KY-1Na (0.06). Density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggested that the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) distributions for the molecular structure of KY-2Na are adequately separated, leading to a decrease in the energy gap (ΔEST) between the singlet state (S1) and the triplet state (T1) that causes efficient intersystem crossing (ISC), compared to that for the molecular structure of KY-1Na. Indeed, time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) calculations demonstrated that the ΔEST(S1–T1) value (0.82 eV) of KY-2Na is smaller than that (0.98 eV) of KY-1Na, resulting in a relatively high ΦΔ value of KY-2Na. Consequently, we demonstrate that phenazine-2,3-diol-based PSs bearing carboxylic acid salts possess high solubility and moderate 1O2 generation ability in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...