Dithiocarbamate-based linear versus macrocyclic architecture: comparative studies and applications in protein interaction and heavy metal removal†
Abstract
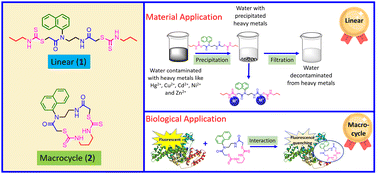
The architecture of molecules plays a significant role in their effective binding with another moiety. Direct comparison of a linear dithiocarbamate and its macrocyclic analogue was carried out, to explore the magnitude of these architectural effects for different biological and material science applications. Linear and macrocyclic compounds with the same functional groups, such as amide, dithiocarbamic ester, naphthyl, and propyl, were designed, synthesized, and compared through their spectral, physicochemical, and thermal properties. Utilizing dithiocarbamates, the compounds were used for the detoxification of water by removal of toxic heavy metals, including Hg2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, and Ni2+ by precipitation. In addition, comparable interactions with various important proteins, such as bovine serum albumin, human serum albumin, haemoglobin, lysozyme, proteinase, ribonuclease, and trypsin, were performed. The observation of better performance for the macrocycle towards protein interaction, and of the linear compound for removal of heavy metals is remarkable, and proves that the compound architecture is important.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...