Pyridyl-benzimidazole derivatives decorated with phenylazo substituents and their low-spin iron(ii) complexes: a study of the synthesis, structure and photoisomerization†
Abstract
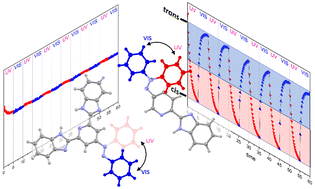
A series of phenylazo-substituted derivatives of pyridyl-benzimidazoles L1–L5 has been synthesized via a modified Mills reaction and their structural, spectral and photoswitching properties were investigated. NMR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis of the desired compounds confirmed their E conformation. The light-induced E ↔ Z (also called trans ↔ cis) isomerization was monitored using UV-VIS and 1H NMR spectroscopy that revealed a reversible photochromic behavior governed by first-order kinetics. State-of-the-art meta-dynamics simulations (iMTD-GC) and ab initio calculations (CASSCF-NEVPT2 and STEOM-DLPNO-CCSD) made the analysis of the electronic structures of ligands possible, which helped to explain the bland E-to-Z conversion of L1 and pronounced switching of L2–L5 ligands. Furthermore, the computational studies identified the active wavelengths of E-to-Z conversion and allowed assessing the mechanisms of photoisomerization. Additionally, ligands L1 and L2 were used for the preparation of four ferrous coordination compounds C1–C4 in which the structural and magnetic investigations confirmed the permanent low-spin state and diamagnetic behavior in the solid state. On the other hand, dissolved compounds C1 and C2 are high-spin at room temperature and their blue light irradiation causes the decomplexation instead of the desired E-to-Z isomerization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...