Dual-infinite coordination polymer-engineered nanomedicines for dual-ion interference-mediated oxidative stress-dependent tumor suppression†
Abstract
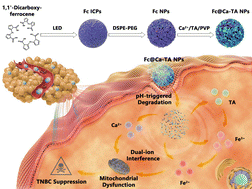
Recently, nanomedicine design has shifted from simple nanocarriers to nanodrugs with intrinsic antineoplastic activities for therapeutic performance optimization. In this regard, degradable nanomedicines containing functional inorganic ions have blazed a highly efficient and relatively safe ion interference paradigm for cancer theranostics. Herein, given the potential superiorities of infinite coordination polymers (ICPs) in degradation peculiarity and functional integration, a state-of-the-art dual-ICP-engineered nanomedicine is elaborately fabricated via integrating ferrocene (Fc) ICPs and calcium–tannic acid (Ca–TA) ICPs. Thereinto, Fc ICPs, and Ca–TA ICPs respectively serve as suppliers of ferrous iron ions (Fe2+) and calcium ions (Ca2+). After the acid-responsive degradation of ICPs, released TA from Ca–TA ICPs facilitated the conversion of released ferric iron (Fe3+) from Fc ICPs into highly active Fe2+. Owing to the dual-path oxidative stress and neighboring effect mediated by Fe2+ and Ca2+, such a dual-ICP-engineered nanomedicine effectively induces dual-ion interference against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Therefore, this work provides a novel antineoplastic attempt to establish ICP-engineered nanomedicines and implement ion interference-mediated synergistic therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...