Acute effects of drinks containing blackcurrant and citrus (poly)phenols and dietary fibre on postprandial glycaemia, gut hormones, cognitive function and appetite in healthy adults: two randomised controlled trials†
Abstract
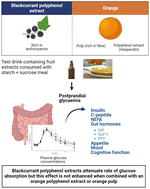
(Poly)phenol (PP)-rich blackcurrant (BC) extracts reduce postprandial glucose concentrations. Combinations with other fruit (poly)phenols and fruit fibre may enhance the effect. This study investigated the acute effects of combinations of BC extracts, high (H-BC) and low (L-BC) (poly)phenol concentrations, sweet orange extracts (SO) and fibre-rich orange pulp (F) in reducing postprandial glycaemia. In two randomised, double-blind, crossover design studies, healthy participants consumed seven types of 200 mL beverages: in the GLU-FX trial, H-BC (1600 mg PP); L-BC (800 mg PP); SO (800 mg PP); BC + SO (1600 mg PP) or CON (placebo); in the GLU-MIX trial, BC + F (800 mg PP), F (1.5 g fibre), or CON2 (placebo), immediately followed by consumption of 75 g available carbohydrate (starch and sugars). Blood was sampled at baseline and postprandially to measure changes in glucose, insulin, and gut hormones; appetite changes were assessed by visual analogue scales and, in GLU-MIX, ad libitum food intake and cognitive function were assessed. Twenty-nine and thirty-seven adults completed GLU-FX and GLU-MIX, respectively. L-BC reduced early postprandial glycaemia (0–30 min) with no differences in glucose incremental Cmax or total glycaemic response. No significant effect was observed following other drinks relative to CON. L-BC and H-BC drinks inhibited insulin secretion up to 30 min and GIP up to 120 min. In GLU-MIX, BC + F improved some indicators of cognitive function but not all. Measures of appetite were unaffected. The impact of (poly)phenol-rich BC extracts on total postprandial glycaemia in healthy participants was minimal and not enhanced when administered in combination with an orange (poly)phenol extract or orange pulp. Clinical Trials registered at https://www.clinicaltrials.gov: NCT03184064 (GLU-FX) and NCT03572296 (GLU-MIX).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...