Maternal supplementation with human milk-derived Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WLPL04 affects the immunity and gut microbiota of offspring rats†
Abstract
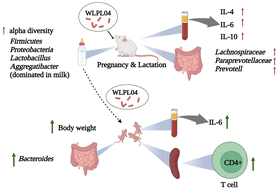
Pregnancy and lactation are a window period during which interventions on mothers bring beneficial effects to newborns. This study aims to investigate the effects of maternal supplementation with human-milk-derived Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WLPL04-36e during pregnancy and lactation on the physiology, immunity and gut microbiota of dams and their offspring. We found that after maternal supplementation, L. plantarum WLPL04-36e could be detected in the intestines and extraintestinal tissues (liver, spleen, kidneys, mammary gland, MLN and brain) of dams, as well as in the intestines of their offspring. Maternal supplementation with L. plantarum WLPL04-36e could significantly increase the body weights of dams and their offspring during the middle to late lactation period, elevate the serum levels of IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 of dams and IL-6 level of offspring, and increase the proportion of spleen CD4+ T lymphocytes of the offspring. Moreover, L. plantarum WLPL04-36e supplementation could increase the alpha diversity of milk microbiota during early and middle lactation periods, and elevated the abundance of Bacteroides in the intestines of offspring at week 2 and week 3 after birth. These results suggest that maternal supplementation with human-milk-derived L. plantarum can regulate the immunity and intestinal microbiota composition of offspring and play positive roles in the growth of offspring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...