Ginsenoside-Rg1 synergized with voluntary running exercise protects against glial activation and dysregulation of neuronal plasticity in depression†
Abstract
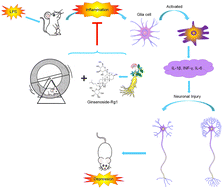
Depression is a common psychological disease accompanied by mental disorders and somatic symptoms. However, the underlying mechanisms regarding the pathogenesis of depression are still not clear. Neuronal damage resulting from inflammation is considered to be one of the important risk factors for depression. Ginsenoside-Rg1, a sterol extract extracted from ginseng herbs, has been shown to have neuroprotective effects against neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, running exercise, a simple behavioral therapy, has been recently shown to have antidepressant effects. However, whether these two synergized strategies are more efficient in depression treatment, especially the neural mechanisms underlying this practical and interesting treatment is unknown. In this study, we have shown that ginsenoside-Rg1 synergized with voluntary running exercise exerts more efficiency on suppressing neuroinflammation, up-regulating expression of neurotrophic factors, and synaptic-related proteins, ameliorating neuronal structural damages than that of ginsenoside-Rg1 or voluntary exercise alone, suggesting its better neuroprotective effects. More importantly, the antidepressant-like effect of this synergistic treatment was also significantly better than either of these two treatments. These results suggest that ginsenoside-Rg1, synergized with voluntary running, may have higher efficacy in the treatment of depression through anti-inflammation and the improvement of neuroplasticity. These findings may provide a new perspective for the development of a therapeutic strategy for depression.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...