A highly specific and flexible detection assay using collaborated actions of DNA-processing enzymes for identifying multiple gene expression signatures in breast cancer†
Abstract
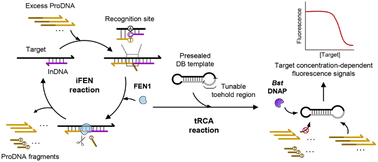
Most nucleic acid biosensors employ nucleic acid-processing enzymes to bind, degrade, splice, synthesize, and modify nucleic acids. Utilizing their unique substrate preference, binding mode, and catalytic activity is of great importance in designing nucleic acid biosensors. Combination with DNA-processing enzymes enables them to transform into a new generation of molecular diagnostics tools with enhanced selectivity and sensitivity and reduced reaction time. Here, we report an isothermal amplification strategy by coemploying a structure-specific endonuclease (flap endonuclease 1, FEN1) and a strand-displacing DNA polymerase (Bst DNA polymerase) to detect long RNA targets. This approach couples the FEN1-driven invasive cleavage reaction with toehold-mediated rolling circle amplification (iFEN–tRCA), enabling the highly selective and rapid detection of long RNA targets and offering a detection limit below 10 pM within 1 h. We used two targets, such as human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2, encoded by ERBB2) and dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP, encoded by PPP1R1B), associated with prognosis or response to anticancer therapy. We demonstrated the feasibility and quantitative capability of the iFEN–tRCA assay by assessing the expression of two RNA transcripts (ERBB2 and PPP1R1B) with total RNA extracts purified from human breast cancer cells. Therefore, we envision that the developed assay will provide a suitable prognostic and diagnostic tool for identifying appropriate patients for HER2-targeted therapy and predicting the clinical outcome and occurrence of metastasis relapse in breast cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...