New insights into structure/optical waveguide behavior relationships in linear bisethynylbenzenes†
Abstract
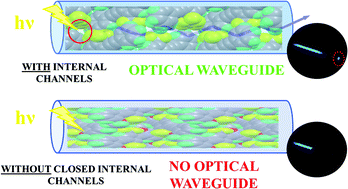
In order to establish a relationship between the structure and the optical waveguiding behavior, two series of linear bisethynylbenzenes combining trifluoromethyl and methoxy groups in the core and external rings were synthesized. The presence of methoxy groups in the core benzene led to the production of, generally, amorphous supramolecular aggregates, while the presence of trifluoromethyl groups in the core benzene led to the production of needle shaped crystals. As a result of this, most planar compounds exhibited optical waveguiding behavior as shown by photoluminescence (PL) microscopy and optical loss coefficients down to 0.54 × 10−3 dB μm−1 in some of them, revealing optical waveguides assets. X-ray diffraction studies were performed to establish a first approximation to the structure/optical property relationships, confirming that the presence of channels in the crystal structure is concomitant with the optical waveguiding behavior. This feature constitutes a relevant parameter to be taken into account to understand light propagation in these structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...