DC bias characteristic enhancement of the powder core by using densified submicron sized FeNi particles through spray pyrolysis†
Abstract
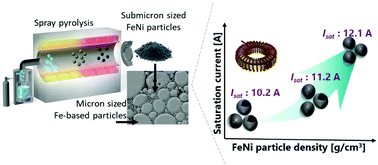
The powder core type of inductor has become a promising component of a high-power DC–DC converter. The inductor consists of a powder core, a packing of primary (coarse) and secondary (fine) particles, and a winding coil. The characteristic of the secondary particles in the powder core is crucial to the inductor performance, i.e., DC bias characteristic. Here, we successfully produce high-density spherical and submicron sized FeNi particles (300–400 nm), which were investigated as the secondary particles for the first time. By precisely controlling the temperature and residence time of the spray pyrolysis process, the size and structure of the FeNi particles were altered owing to densification. The structural change from hollow to dense provides a stable magnetic characteristic of the FeNi particles at 1.5 T with an enhancement of the particle density from 7.38 to 8.33 g cm−3. As a result, the as-prepared FeNi particles exhibit an excellent DC bias characteristic that is proportional to the escalating particle density. A suppression of the formation of hollow particles from 34% to 10% reveals an improvement in the saturation current (Isat) by approximately 20% from 10.2 A to 12.1 A. The densification not only enlarges the magnetic field path but also increases the adjacent non-magnetic region. The use of the dense and submicron sized spherical FeNi particles is proposed to lead to a wide application for the advancement of renewable energy generators, electric transportations, and electronic devices in industrial sectors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...