Size effect of liposomes on centimeter-deep ultrasound-switchable fluorescence imaging and ultrasound-controlled release†
Abstract
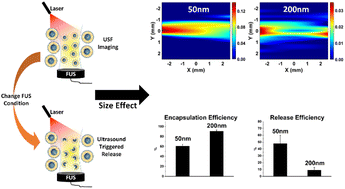
Liposomes have been widely used in both medical imaging and drug delivery fields due to their excellent biocompatibility and easy surface modification. Recently our lab reported for the first-time the implementation of temperature-sensitive and indocyanine green (ICG)-encapsulated liposome microparticles for in vivo ultrasound-switchable fluorescence (USF) imaging. A previous study showed that liposome microparticles achieved USF imaging in centimeter-deep tissue. This study aimed to control the size of liposomes at the nanoscale and study the size effect on the USF imaging depth. Also, we explored the feasibility of combining USF imaging with ultrasound-controlled release. Liposomes were synthesized via the hydration method and the size was controlled by an extruding process. Characterization parameters, including fluorescence profile, spectra, size, stability, encapsulation efficiency, and ultrasound-controlled release, were evaluated. USF imaging in blood serum was conducted successfully in a phantom model, and an imaging depth study was conducted at 1.0 cm and 2.5 cm and confirmed that nano-sized liposomes had a stronger USF signal than micron-sized liposomes. Additionally, releasing tests indicated that both ultrasound power and exposure time affected the release efficiency in that increasing the power and extending the exposure time led to higher release efficiency. Above all, this study shows the potential for using liposomes for USF imaging and ultrasound-controlled release.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...