A natural polysaccharide-based antibacterial functionalization strategy for liquid and air filtration membranes†
Abstract
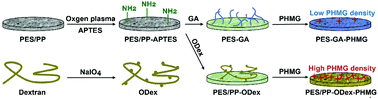
Filtration membranes are widely applied in medical fields. However, these membranes are challenged by bacterial contamination in hospitals, which increases the risk of nosocomial infections. Thus, it is significant to develop antibacterial filtration membranes. In this work, an oxidated dextran (ODex)-based antibacterial coating was designed and constructed on microfiltration (MF) membranes and melt-blown fabrics. Polyhexamethylene guanidine (PHMG) was synthesized as an antibacterial agent, and was fixed by ODex onto filtration membranes. The functionalized MF membranes increased the filtration efficiency for E. coli from 20.9% to 99.9%, and improved the absorption ratio for endotoxin by 59.1%, while the water flow rate still remained as high as 5255 L (h m2)−1. Furthermore, the trapped bacteria were inactivated by the antibacterial coating. For the melt-blown fabrics, the aerosol filtration efficiency was increased from 74.6% to 81.0%, and the antibacterial efficiency was promoted to 92.0%. The present work developed a facile and universal antibacterial functionalization strategy for filtration membranes, which provided a new method for the design and development of various novel antibacterial filtration materials in the medical field.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioinspired Surfaces Engineering for Biomaterials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...