A functional electrolyte additive enabling robust interphases in high-voltage Li‖LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 batteries at elevated temperatures†
Abstract
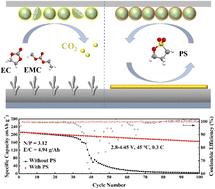
Lithium metal batteries (LMBs) with Ni-rich cathode materials providing ultra-high energy density (∼500 W h kg−1) are expected to be the next generation of batteries. However, high-voltage LMBs exhibit inferior electrochemical performance at elevated temperatures, due to severe dendrite growth in lithium metal anodes and the structural degradation of Ni-rich cathodes, which should be paid attention to in terms of their practical application. Herein, by introducing 1,3-propane sultone (PS) into the carbonate electrolytes, satisfying cycling stability of Li‖LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811) batteries at a high cut-off voltage of 4.45 V and an elevated temperature of 45 °C was achieved, which also shows higher ionic conductivity, wettability and thermodynamic stability. This approach enables uniform lithium plating/stripping at elevated temperatures, because of the construction of a LiF/Li2SO3-rich interphase layer. Besides, PS inhibits drastic structural change and interfacial side reactions on NCM811. It is also noteworthy that Li‖NCM811 full cells delivered decent performance at high-load cathodes, ultra-thin lithium anodes and lean electrolytes cycling at 4.45 V and 45 °C. This strategy provides a feasible solution for boosting high energy density LMBs under extreme conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...