Water oxidation of visible-light-responsive bismuth-yttrium oxychloride promoted by a dual-ion doping strategy for assembly of Z-scheme overall water splitting†
Abstract
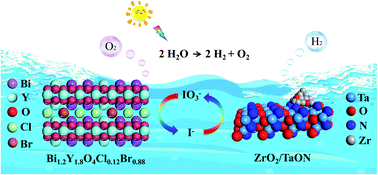
Bismuth yttrium oxychloride (Bi2YO4Cl) is one of the most popular visible-light-responsive photocatalysts; however, it is still challenging to use it in the construction of overall water splitting (OWS) systems. Herein, we introduce a novel dual-ion doping strategy to modulate its structure and water oxidation activity, based on which a feasible Z-scheme OWS system can be assembled. In particular, the doping effect of dual ions (Y3+ and Br−) on the structure and water splitting performance was examined and discussed by combining various characterization studies such as photoelectrochemical current, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, (time-resolved) photoluminescence spectra, and density functional theory calculations. It was observed that a clear synergistic promotion effect occurs on the dual ion-doped sample (Bi3−xYxO4Cl1−yBry), making it exhibit a significantly higher O2 evolution rate compared to a single ion-doped sample. The activity was also observed to strongly depend on the content of dual ions, and the optimized Bi1.2Y1.8O4Cl0.88Br0.12 sample exhibited a remarkable visible-light-responsive O2 production rate of 116 μmol h−1 (the apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) = 5.4% at 420 nm), which was 10 and 20 times higher than those of the Br-/Y-doped sample and pristine Bi2YO4Cl, respectively. The substantially promoted charge separation and reduced activation energy were demonstrated to be responsible for the excellent O2-evolution rate. Finally, we successfully fabricated a feasible Z-scheme OWS system based on the colorless IO3−/I− shuttle redox pair by employing modified Bi1.2Y1.8O4Cl0.88Br0.12 as the O2-evolving photocatalyst along with ZrO2/TaON as the H2-evolving photocatalyst. The dual-ion doping strategy may be extended to several other photocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...