Pt doping and strong metal–support interaction as a strategy for NiMo-based electrocatalysts to boost the hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solution†
Abstract
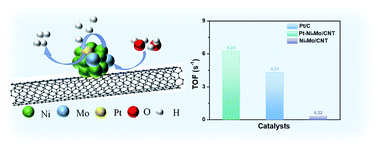
Although extensive research has been carried out on non-noble metal-based materials in the alkaline electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), designing electrocatalysts that have excellent stability and intrinsic activity exceeding that of Pt/C is still an urgent challenge. Herein, we developed a novel strategy to resolve these two problems, which combines Pt doping and a strong metal–support interaction (SMSI). By a simple, quick (60 s) and solvent-free microwave reduction method, Pt–Ni4Mo/CNT with small size (3–4 nm) was prepared and exhibits an extremely low overpotential of 18.6 mV at 10 mA cm−2 in 1 M KOH. In addition, the catalyst has a large turnover frequency value at an overpotential of 100 mV, which is higher than that of Pt/C (4.31 s−1). Benefiting from the SMSI, the catalytic activity of the catalyst can be maintained for 200 h at 100 mA cm−2, indicating that the catalyst has excellent stability. Finally, in situ attenuated total reflection surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy (ATR-SEIRAS) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrated that the Ni4Mo site mainly plays the role of dissociating water in the process of the HER to produce H* and OH*, then the strongly adsorbed H* intermediate is transferred to the Pt site, not only exposing the active center on Ni4Mo but accelerating the H2 desorption process. This original strategy will provide valuable inspiration for the design and synthesis of other catalysts in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...