Tuning the Co/Fe ratio in BaCoxFe0.8−xZr0.1Y0.1O3−δ, a promising triple ionic and electronic conducting oxide, to boost electrolysis and fuel cell performance†
Abstract
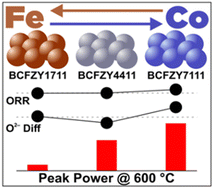
The triple conducting oxide BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3−δ (BCFZY4411), which accommodates simultaneous transport of protons, oxygen ions, and p-type electronic carriers, has been intensively investigated in recent years as a high-performance positive electrode material for fuel cell and electrolysis applications. The heavy Co and Fe-based transition metal doping in BCFZY4411 ensures adequate electrical conductivity while the multiple oxidation states of Co and Fe assist the electrocatalytic and redox ability. Despite the considerable role of Co and Fe transition metal doping in controlling electrochemical activity, however, the study of alternative BCFZY compositions with varying Co/Fe ratios has not yet been pursued. Here, we evaluate the electrochemical performance of a series of BaCoxFe0.8−xZr0.1Y0.1O3−δ compositions with varying Co/Fe ratio (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.7) and use oxygen ion tracer diffusion and in situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction to investigate the effect of Co/Fe ratio on electrocatalytic activity, electronic conductivity, oxygen ion incorporation and transport kinetics, and thermomechanical behavior. We find that Co-rich BCFZY7111 yields the highest performance due to exceptionally high oxygen vacancy diffusion and shows a lower and more linear thermal expansion behavior compared to Fe-rich compositions. A protonic ceramic button cell incorporating a BCFZY7111 positive electrode yields a peak power density of 695 mW cm−2 under fuel cell mode and an electrolysis current density of 1976 mA cm−2 at 1.4 V at 600 °C, underscoring the promise of this new BCFZY electrode composition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...