Highly efficient extraction of uranium from aqueous solution using imidazole functionalized core–shell sunflower-like superparamagnetic polymer microspheres: understanding adsorption and binding mechanisms†
Abstract
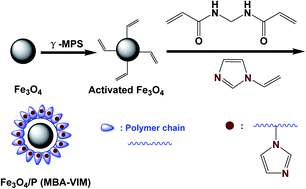
Recovery of uranium from aqueous solutions using core–shell superparamagnetic polymer nanomaterials as efficient adsorbents might be helpful for environmental protection, due to their excellent structural stability, high concentration of accessible organic ligands and superparamagnetic character. Herein, a novel imidazole functionalized core–shell sunflower-like magnetic polymer adsorbent Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM) was synthesized by one step distillation-precipitation polymerization of N,N′-methylene bis(2-propenamide) (MBA) and vinyl imidazole (VIM). The magnetic Fe3O4 core facilitated easy separation by using magnetic force. The polymer shell with a sunflower-like structure provided relatively large specific surface area and abundant active adsorption sites, and the high concentration of imidazole groups could function as a claw for catching uranium. The maximum adsorption capacity of 800.0 mg g−1 on Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM) could be attained at pH 4.5, and adsorption equilibrium could be achieved even within 180 seconds, which was far superior to that of most of the adsorbents reported previously. Besides, Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM) also showed an excellent uranium selectivity of 84.2% in the presence of multiple ions, and could be isolated by using magnetic force facilely and be recycled for at least six cycles without an obvious decrease of adsorption capacity. More importantly, Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM) had an excellent structural stability, and the morphology and chemical structure of the adsorbent did not change even after six cycles. Both XPS and DFT analysis confirmed that only the N atom in C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N of imidazole took part in uranium coordination. The DFT result showed the optimized geometric structure of 1 : 2 of UO22+ with the two imidazole groups of the two distinct polymer chains which could describe the interaction of uranium with Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM). Thus, this work provides a convenient strategy to develop core–shell magnetic adsorbents for efficient extraction of uranium from aqueous solutions.
N of imidazole took part in uranium coordination. The DFT result showed the optimized geometric structure of 1 : 2 of UO22+ with the two imidazole groups of the two distinct polymer chains which could describe the interaction of uranium with Fe3O4/P (MBA-VIM). Thus, this work provides a convenient strategy to develop core–shell magnetic adsorbents for efficient extraction of uranium from aqueous solutions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...