Li-ion conductivity in Li2OHCl1−xBrx solid electrolytes: grains, grain boundaries and interfaces†
Abstract
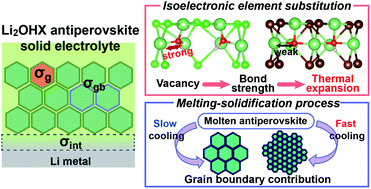
In this study, we conduct a comprehensive investigation of the effect of grain, grain boundary and interfacial resistance on the total Li-ion conductivity in Li2OHCl1−xBrx antiperovskite solid electrolytes. We highlight how the thermal expansion coefficient can serve as an indicator for the presence of structural defects, which are difficult to probe directly with X-ray techniques, and their effect on bulk Li-ion conduction. The detrimental effect of grain boundaries on ionic conductivity is investigated by atomistic calculations and validated experimentally by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy on pellets with controlled grain size. The effect of composition on interfacial resistance is probed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. These insights provide design principles to improve Li-ion conductivity in lithium hydroxide halide antiperovskites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...