Crosslinked xylose-based polyester as a bio-derived and degradable solid polymer electrolyte for Li+-ion conduction†
Abstract
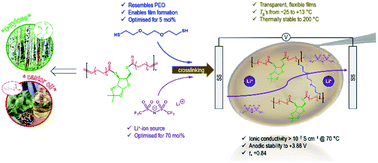
A novel crosslinked polyester derived from D-xylose and 10-undecenoic acid (from castor oil) has been investigated as a new material for solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) applications. Acyclic diene metathesis polymerisation of a bio-derived monomer, followed by crosslinking with 2,2-(ethylenedioxy)diethanethiol (to impart film properties and mechanical strength) and incorporation of lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI), resulted in flexible and transparent SPE films. The materials exhibited Tg's between −25 °C and 13 °C and thermal stability up to 234 °C. Ionic conductivity was measured as a function of molar mass, crosslinking density and salt molarity which were optimised to achieve an ionic conductivity as high as 1.0 × 10−5 S cm−1 at 60 °C. A high lithium transference number of 0.84 was also achieved and electrochemical stability up to 3.88 V was demonstrated. Revealing 33% of the xylofuranose core OH groups via ketal deprotection resulted in a semi-crystalline polymer whose crystallinity was disrupted by incorporation of LiTFSI. The resulting SPE material offered a small, yet non-significant, improvement of ionic conductivity (3.5 × 10−5 S cm−1vs. 1.0 × 10−5 S cm−1 at 60 °C).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...