Inducing atomically dispersed Cl–FeN4 sites for ORRs in the SiO2-mediated synthesis of highly mesoporous N-enriched C-networks†
Abstract
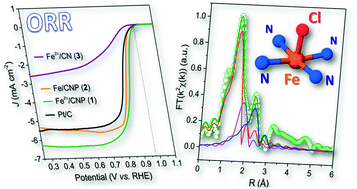
Atomically dispersed iron sites within N-enriched C-networks are promising low-cost catalytic materials for electrochemical applications. At odds with their often-outstanding performance in challenging electrocatalytic processes (i.e. oxygen reduction reaction, ORR) their fabrication strategy frequently relies on trial-and-error approaches. Moreover, the complex chemical nature of these hybrids is often dictated by the use of highly aggressive etching/doping thermo-chemical treatments. Therefore, the development of simplified chemical protocols based on cheap and abundant raw materials ensuring highly reproducible synthetic paths with the prevalent generation of discrete single-atom sites in a definite coordination environment remains a challenging issue to be properly addressed. In this contribution, the synthesis of hierarchically porous and N-enriched C-networks prevalently containing Cl–FeN4 sites is proposed. The outlined procedure takes advantage of citrate ions as carriers for N-sites and a sacrificial C-source for the synthesis of N/C matrices. At the same time, the chelating character of citrate polyions fosters the complexation of transition metals for their ultimate atomic dispersion in C/N matrices. The procedure is finally adapted to the use of common inorganic hard templates and porogens for the control of the material morphology. Avoiding any thermo-chemical etching/doping phase, the as-prepared catalytic material has shown remarkably high ORR performance in an alkaline environment. With a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.88 V, a kinetic current density up to 109.6 A g−1 (normalized to the catalyst loading at 0.8 V vs. RHE) and outstanding stability, it largely outperforms commercial Pt/C catalysts and certainly ranks among the most performing ORR Fe-single-atom-catalysts (Fe-SACs) reported so far.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Single-Atom Catalysis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...