Synthetic solid oxide sorbents for CO2 capture: state-of-the art and future perspectives
Abstract
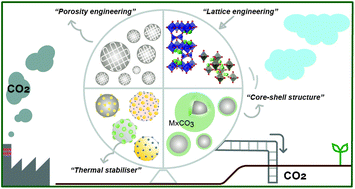
Carbon capture is an important and effective approach to control the emission of CO2 from point sources such as fossil fuel power plants, industrial furnaces and cement plants into the atmosphere. For an efficient CO2 capture operation, many aspects of the CO2 capture steps need to be carefully considered. Currently the most mature CO2 capture technology is liquid amine scrubbing. Alternatively, solid sorbents can be used to effectively capture CO2 while alleviating the disadvantages associated with liquid amine sorbents. In this review, we critically assess solid metal oxide CO2 sorbents, especially oxides of group 1 (Li, Na and K) and group 2 (Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba) metals, for capturing CO2 at moderate to high temperatures. In particular, we focus on the recent advances in developing synthetic metal oxide sorbents, and the correlation between the design, synthetic approaches and their cyclic CO2 capture performance, which are characterised by CO2 uptake capacity, rate of carbonation and cyclic stability. The state-of-the-art, challenges, opportunities and future research directions for these metal oxide sorbents are discussed. By devoting more research effort to address the issues identified, there can be great potential to utilise Group 1 and 2 metal oxides as cost-effective, highly efficient sorbents for CO2 capture in a variety of carbon capture applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Lunar New Year collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...