3D structural lithium alginate-based gel polymer electrolytes with superior high-rate long cycling performance for high-energy lithium metal batteries†
Abstract
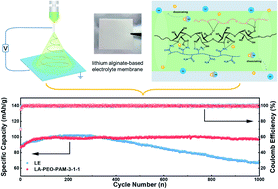
The development of polymer electrolytes with good ion transport capacity and high mechanical strength is a big challenge for solid polymer electrolytes. Herein, a natural polymer-based gel electrolyte (GPE) with a three-dimensional nanostructure and higher ionic conductivity is developed. The electrospinning technique is used to prepare the composite GPEs containing lithium alginate (LA), poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and polyacrylamide (PAM). Thanks to the synergistic transportation of Li ions by LA and PAM, as well as enhanced mechanical strength by a strong hydrogen bond between LA and PAM, the as-prepared electrolyte membrane possesses high ion transport capacity and the ability to impede the growth of lithium dendrites. Specifically, the ionic conductivity of the optimized LA–PEO–PAM-3-1-1 GPE goes up to 2.86 mS cm−1 at 30 °C, and the lithium ion transference number reaches 0.59. Importantly, the LFP/LA–PEO–PAM-3-1-1/Li cells maintain a stable discharge specific capacity of 100 mA h g−1 for 1000 cycles at a high rate of 10C. The GPE also delivers good compatibility with the NCM523 cathode. Furthermore, LFP/LA–PEO–PAM-3-1-1/Li pouch cells could light LED bulbs in critical situations such as blending, piercing, and cutting. The results reveal that the lithium alginate-based GPEs have the potential to be applied in commercial lithium batteries with high performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...