Morphological signatures of actin organization in single cells accurately classify genetic perturbations using CNNs with transfer learning†
Abstract
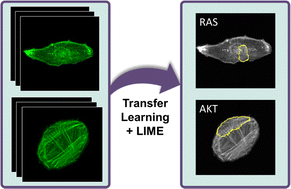
The actin cytoskeleton plays essential roles in countless cell processes, from cell division to migration to signaling. In cancer cells, cytoskeletal dynamics, cytoskeletal filament organization, and overall cell morphology are known to be altered substantially. We hypothesize that actin fiber organization and cell shape may carry specific signatures of genetic or signaling perturbations. We used convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on a small fluorescence microscopy image dataset of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells for identifying morphological signatures in cancer cells. Using a transfer learning approach, CNNs could be trained to accurately distinguish between normal and oncogenically transformed RPE cells with an accuracy of about 95% or better at the single cell level. Furthermore, CNNs could distinguish transformed cell lines differing by an oncogenic mutation from each other and could also detect knockdown of cofilin in TNBC cells, indicating that each single oncogenic mutation or cytoskeletal perturbation produces a unique signature in actin morphology. Application of the Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME) method for visually interpreting the CNN results revealed features of the global actin structure relevant for some cells and classification tasks. Interestingly, many of these features were supported by previous biological observation. Actin fiber organization is thus a sensitive marker for cell identity, and identification of its perturbations could be very useful for assaying cell phenotypes, including disease states.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...