Spontaneous formation and growth kinetics of lipid nanotubules induced by passive nanoparticles†
Abstract
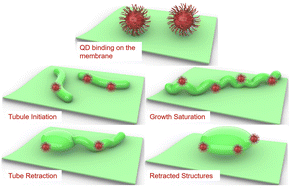
Lipid nanotubules (LNTs) are conduits that form on the membranes of cells and organelles, and they are ubiquitous in all forms of life from archaea and bacteria to plants and mammals. The formation, shape and dynamics of these LNTs are critical for cellular functions, supporting the transport of myriad cellular cargoes as well as communication within and between cells, and they are also widely believed to be responsible for exploitation of host cells by pathogens for the spread of infection and diseases. In vitro kinetic control of LNT formation can considerably enhance the scope of utilization of these structures for disease control and therapy. Here we report a new paradigm for spontaneous lipid nanotubulation, capturing the dynamical regimes of growth, stabilization and retraction of the tubes through the binding of synthetic nanoparticles on supported lipid bilayers (SLBs). The tubulation is determined by the spontaneous binding–unbinding of nanoparticles on the LNTs. The presented methodology could be used to rectify malfunctioning cellular tubules or to prevent the pathogenic spread of diseases through inhibition of cell-to-cell nanotubule formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...