Anionically modified N-(alkyl)acrylamide-based semi-IPN hybrid gels reinforced with SiO2 for enhanced on–off switching and responsive properties†
Abstract
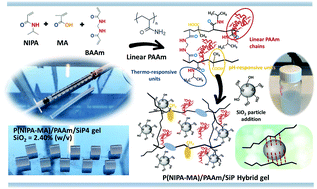
Semi-interpenetrated (semi-IPN) poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid)/polyacrylamide P(NIPA–MA)/PAAm hybrid gels containing linear poly(acrylamide) PAAm chains were designed by incorporation of different amounts of silica particles (SiP). Formation of temperature-sensitive semi-IPN hybrid gels was evaluated by simultaneous radical polymerization under different polymerization temperatures, and the effect of polymer/particle interfaces on the swelling and elasticity was explained. Nanoparticle-mediated enhancements were studied to understand the effect of addition of SiP to anionically modified semi-IPNs. Hybrid network formation was confirmed by FTIR, with an increase in SiP resulting in an increased Si–O–Si absorption peak in hybrid samples. P(NIPA–MA)/PAAm/SiP gels showed a reduction in the degree of swelling with the addition of SiP. The Flory–Huggins interaction parameter of the semi-IPN hybrid-solvent was estimated using the extended equation. The compression test results showed an improvement in the stiffness and modulus attributed to stress transfer from the hybrid network to nanoparticles. Swelling processes of semi-IPN hybrids prepared by cold polymerization have anomalous diffusion owing to polymer relaxation, while Fickian behavior was observed for the hybrids obtained by warm polymerization. During oscillation shrinking–swelling of semi-IPN hybrids upon ionic-strength switching in NaCl solutions, the gels retained their shape and integrity for 10 cycles of testing. To evaluate the adsorption characteristics of semi-IPN hybrids, methyl violet (MV) was chosen as a model cationic dye. The effects of contact time, silica content and initial dye concentration were studied and the time-dependent adsorption data were fitted with six kinetic models. The MV uptake capacity of semi-IPN hybrids increased with an increase in the initial MV concentration as well as with silica content. The adsorption process followed pseudo-second order type adsorption kinetics and the mechanism of process was better described by intraparticle diffusion. These results will contribute to the understanding of roles of anionic comonomer and linear polymer doping in nanoparticle-mediated synthesis of hybrid gels and to the development of next-generation materials for pharmaceutical and environmental-based applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...