Dual-reactive nanogels for orthogonal functionalization of hydrophilic shell and amphiphilic network†
Abstract
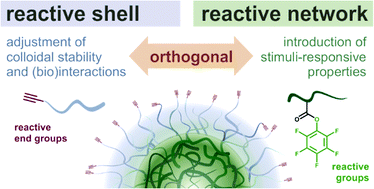
Amphiphilic nanogels (NGs) combine a soft, water-swollen hydrogel matrix with internal hydrophobic domains. While these domains can encapsulate hydrophobic cargoes, the amphiphilic particle surface can reduce colloidal stability and/or limit biological half-life. Therefore, a functional hydrophilic shell is needed to shield the amphiphilic network and tune interactions with biological systems. To adjust core and shell properties independently, we developed a synthetic strategy that uses preformed dual-reactive nanogels. In a first step, emulsion copolymerization of pentafluorophenyl methacrylate (PFPMA) and a reduction-cleavable crosslinker produced precursor particles for subsequent network modification. Orthogonal shell reactivity was installed by using an amphiphilic block copolymer (BCP) surfactant during this particle preparation step. Here, the hydrophilic block poly(polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate) (PPEGMA) contains a reactive alkyne end group for successive functionalization. The hydrophobic block (P(PFPMA-co-MAPMA) contains random methacryl-amido propyl methacrylamide (MAPMA) units to covalently attach the surfactant to the growing PPFPMA network. In the second step, orthogonal modification of the core and shell was demonstrated. Network functionalization with combinations of hydrophilic (acidic, neutral, or basic) and hydrophobic (cholesterol) groups gave a library of pH- and redox-sensitive amphiphilic NGs. Stimuli-responsive properties were demonstrated by pH-dependent swelling and reduction-induced degradation via dynamic light scattering. Subsequently, copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition was used to attach azide-modified rhodamine as model compound to the shell (followed by UV-Vis). Overall, this strategy provides a versatile platform to develop multi-functional amphiphilic nanogels as carriers for hydrophobic cargoes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...