Zintl cluster supported low coordinate Rh(i) centers for catalytic H/D exchange between H2 and D2†
Abstract
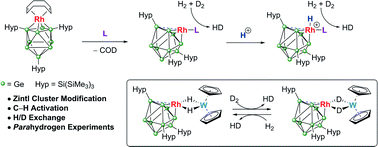
Ligand exchange reactions of [Rh(COD){η4-Ge9(Hyp)3}] with L-type nucleophiles such as PMe3, PPh3, IMe4 (IMe4 = 1,3,4,5-tetramethylimidazol-2-ylidene) or [W(Cp)2H2] result in the displacement of the COD ligand to afford clusters with coordinatively unsaturated trigonal pyramidal rhodium(I) centers [Rh(L){η3-Ge9(Hyp)3}]. These species can be readily protonated allowing access to cationic rhodium–hydride complexes, e.g. [RhH(PPh3){η3-Ge9(Hyp)3}]+. These clusters act as catalysts in H/D exchange between H2 and D2 and alkene isomerisation, thereby illustrating that metal-functionalized Zintl clusters are active in both H–H and C–H bond activation processes. The mechanism of H/D exchange was probed using parahydrogen induced polarization experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...