Biohybrid photosynthetic charge accumulation detected by flavin semiquinone formation in ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase†
Abstract
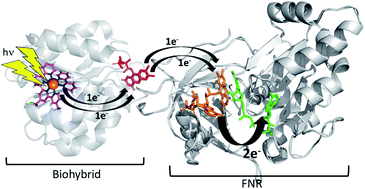
Flavin chemistry is ubiquitous in biological systems with flavoproteins engaged in important redox reactions. In photosynthesis, flavin cofactors are used as electron donors/acceptors to facilitate charge transfer and accumulation for ultimate use in carbon fixation. Following light-induced charge separation in the photosynthetic transmembrane reaction center photosystem I (PSI), an electron is transferred to one of two small soluble shuttle proteins, a ferredoxin (Fd) or a flavodoxin (Fld) (the latter in the condition of Fe-deficiency), followed by electron transfer to the ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (FNR) enzyme. FNR accepts two of these sequential one electron transfers, with its flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor becoming doubly reduced, forming a hydride which is then passed onto the substrate NADP+ to form NADPH. The two one-electron potentials (oxidized/semiquinone and semiquinone/hydroquinone) are similar to each other with the FNR protein stabilizing the hydroquinone, making spectroscopic detection of the intermediate semiquinone state difficult. We employed a new biohybrid-based strategy that involved truncating the native three-protein electron transfer cascade PSI → Fd → FNR to a two-protein cascade by replacing PSI with a molecular Ru(II) photosensitizer (RuPS) which is covalently bound to Fd and Fld to form biohybrid complexes that successfully mimic PSI in light-driven NADPH formation. RuFd → FNR and RuFld → FNR electron transfer experiments revealed a notable distinction in photosynthetic charge accumulation that we attribute to the different protein cofactors [2Fe2S] and flavin. After freeze quenching the two-protein systems under illumination, an intermediate semiquinone state of FNR was readily observed with cw X-band EPR spectroscopy. The increased spectral resolution from selective deuteration allowed EPR detection of inter-flavoprotein electron transfer. This work establishes a biohybrid experimental approach for further studies of photosynthetic light-driven electron transfer chain that culminates at FNR and highlights nature's mechanisms that couple single electron transfer chemistry to charge accumulation, providing important insight for the development of photon-to-fuel schemes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...