Synthesis of a porous SiO2–H3BO3–V2O5–P2O5 glassy composite: structural and surface morphological behaviour for CO2 gas sensing applications†
Abstract
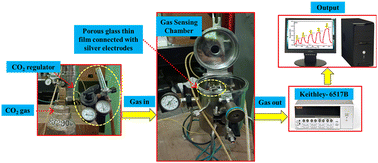
The present work mainly focuses on the fabrication of a porous glass 40SiO2–35H3BO3–19V2O5–6P2O5 via a melt-quenching technique. The structural, morphological, and sensing behaviour of the glass sample was investigated successfully. The calculated density and molar volume of the fabricated glass are 2.4813 ± 0.124 g cm−3 and 35.7660 ± 1.708 cm3 mol−1. XRD, SEM and TEM analyses confirmed the amorphous nature of the glass. FTIR results revealed the O–H bond formations, which indicate that the presence of water molecules is probably due to the porous nature of the glass. Further, BET analysis confirmed the mesoporous nature of the glass sample with a mean pore diameter of 7 nm. The sensing response of the synthesized glass at 1000 ppm concentration of CO2 was found to be 3.05 with a response time 22.6 s and recovery time 25.8 s. Hence, this porous glass can be easily synthesized, is affordable, and was found to be useful for CO2 gas sensing applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...