In silico investigation of the role of vitamins in cancer therapy through inhibition of MCM7 oncoprotein†
Abstract
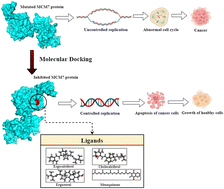
An overabundance of MCM7 protein, a component of the minichromosome maintenance complex that normally initiates DNA replication, has been reported to cause different types of cancers with aggressive malignancy. Inhibition of MCM7 may lead to a significant reduction in cancer-associated cell proliferation. Despite such significance of MCM7 in cancer, the protein structure is yet to be resolved experimentally. This significantly halts the structure-guided ligand designing for cancer therapy targeting the MCM7. The present study aims to resolve the tertiary structure of MCM7 and repurpose the FDA-approved clinically used drugs for cancer therapy by targeting MCM7 protein. The secondary and 3D structures of MCM7 were generated using multiple bioinformatics tools, including the Self-Optimized Prediction Method with Alignment (SOPMA), SWISS-MODEL, and I-TASSER. The reliability of the modeled structure was assessed using PROCHECK. Initially, a structure-guided virtual screening was performed on the approved drug library to identify potential hits against MCM7. The detailed molecular mechanism of receptor interactions of the identified hits was evaluated using extensive molecular dynamics simulation. The results from this study reveal an intriguing discovery of the potential of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2), cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), ergosterol (precursor of vitamin D2) and menaquinone (vitamin K2) as oncoprotein inhibitors for cancer therapy via inhibition of MCM7.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...